Chart
Overview
The following io.keikai.api.model.Range methods allow you to add, move, and delete a chart:
public Chart addChart(SheetAnchor anchor, Type type, Grouping grouping,
LegendPosition pos);
public void deleteChart(Chart chart);
public void moveChart(SheetAnchor anchor,Chart chart);
Supported Chart Types
- AREA
- BAR
- BUBBLE
- COLUMN
- DOUGHNUT
- LINE
- PIE
- SCATTER
All type constants are listed in io.keikai.api.model.Chart.Type.
Supported grouping
STANDARD, STACKED, PERCENT_STACKED and, CLUSTERED. (See io.keikai.api.model.Chart.Grouping)
Supported legend positions
BOTTOM, LEFT, RIGHT, TOP, and TOP_RIGHT (See io.keikai.api.model.Chart.LegendPosition).
Positions
A chart io.keikai.api.model.Chart is a simple object that you can only
get its ID and position. The io.keikai.api.SheetAnchor represents a chart’s position on a sheet.
When adding or moving a chart, you must provide one SheetAnchor to assign
a chart’s position. You can create a SheetAnchor by passing 4 index numbers,
left-top corner’s and right-bottom’s row and column of a chart. When invoking addChart(),
you will get the newly-created chart object in returned value. You had
better store it somewhere you can retrieve it back later if you plan to
delete or move it. Otherwise, you can only get them from a Sheet method:
public List<Chart> getCharts();
Then, use its ID or position to identify a chart.
ZK Charts engine
Keikai uses ZK Charts as the default chart engine.
Example
The screenshot below is a application that can add, move and delete a chart. For simplicity, this application only adds pie charts.
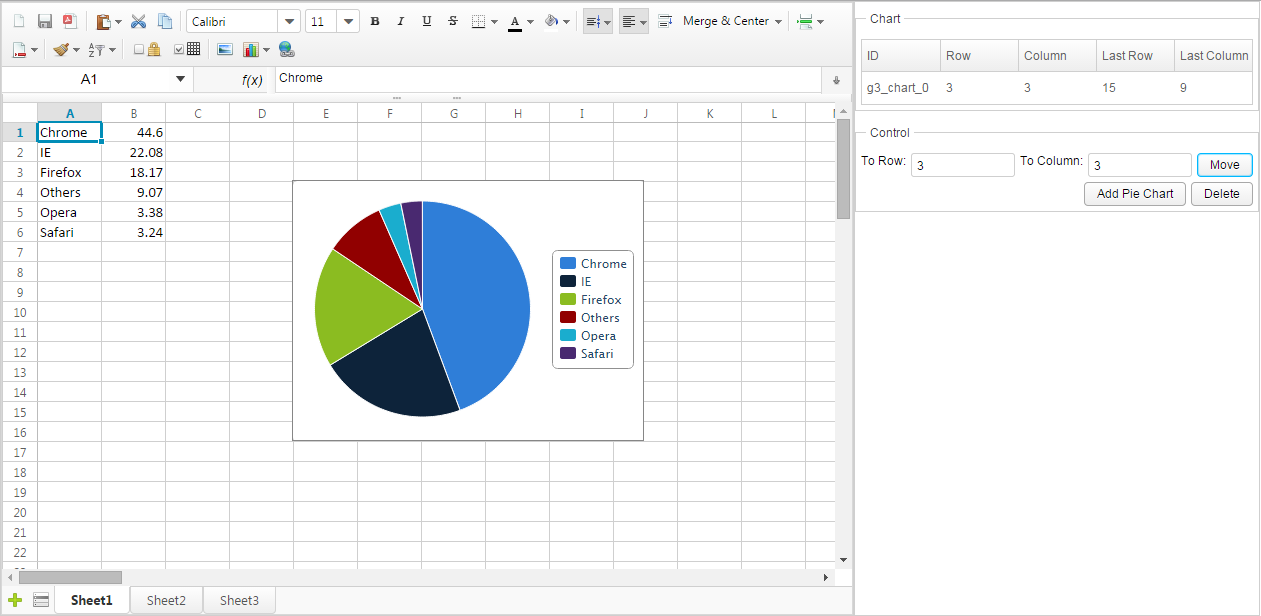
When we click “Add”, it will add a pie chart with the data from A1:B6 and add a items in the Listbox on the top right corner. Select a chart item in the listbox, enter destination row and column index in 2 Intboxes, then click “Move”. The selected chart will be moved to specified position. The “Delete” button will delete the selected chart.
Notice that there are 5 columns in the Listbox on the top right corner
which display information about charts we add. The ID is a chart’s ID
generated automatically by Spreadsheet. The row and column represents a
chart’s position of the left top corner in 0-based index and the last
row and last column represents right bottom corner.
For example, in the screenshot, the topmost chart whose
ID is “rid1”, its left top corner is at “F1” represented in column index
“5” and row index “0”. Its right bottom corner is at “K9” represented in
column index “10” and row index “8”. in column index “1” and row index
“6”. Its right bottom corner is at “C12” represented in column index
“11” and row index “2”. These position information is stored in
SheetAnchor. When adding or moving a picture, you must provide one
SheetAnchor to assign a picture’s position. The SheetOperationUtil
provides methods to simplify this.
Let’s see this application’s controller codes:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
public class ChartComposer extends SelectorComposer<Component> {
@Wire
private Intbox toRowBox;
@Wire
private Intbox toColumnBox;
@Wire
private Spreadsheet ss;
@Wire
private Listbox chartListbox;
private ListModelList<Chart> chartList = new ListModelList<Chart>();
@Listen("onClick = #addButton")
public void addByUtil(){
SheetOperationUtil.addChart(Ranges.range(ss.getSelectedSheet(),
new AreaRef("A1:B6")),
Type.PIE, Grouping.STANDARD, LegendPosition.RIGHT);
refreshChartList();
}
@Listen("onClick = #moveButton")
public void moveByUtil(){
if (chartListbox.getSelectedItem() != null){
SheetOperationUtil.moveChart(Ranges.range(ss.getSelectedSheet()),
(Chart)chartListbox.getSelectedItem().getValue(),
toRowBox.getValue(), toColumnBox.getValue());
refreshChartList();
}
}
@Listen("onClick = #deleteButton")
public void deleteByUtil(){
if (chartListbox.getSelectedItem() != null){
SheetOperationUtil.deleteChart(Ranges.range(ss.getSelectedSheet()),
(Chart)chartListbox.getSelectedItem().getValue());
refreshChartList();
}
}
private void refreshChartList(){
chartList.clear();
chartList.addAll(ss.getSelectedSheet().getCharts());
chartListbox.setModel(chartList);
}
}
- Line 16:
SheetOperationUtil.addChart()converts a range of cells automatically to chart data based on a predefined assumption. For example, it will assume that the first column contains category labels.
Display Empty Values as Gap or Zero
since 5.3.0
Default: false
When a chart’s data source contains a blank cell (empty value), Keikai displays it as 0. You can choose to display it as a gap like:
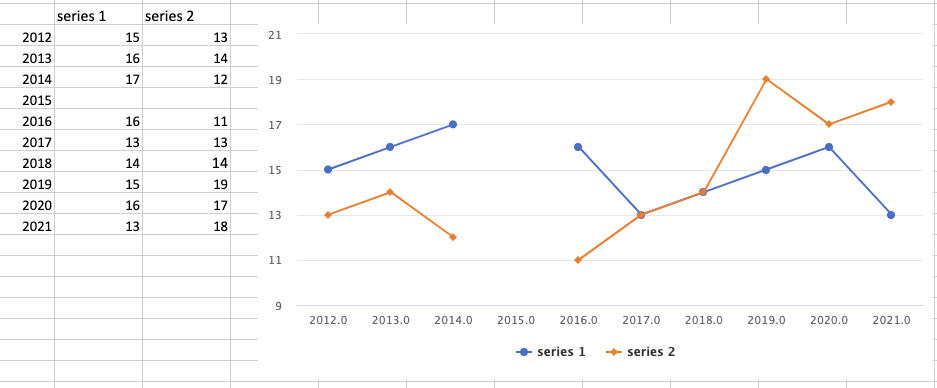
- Limitation: Combo charts don’t support this property.
There are several ways to configure depending on how big scope you want to apply:
Page Scope
Put the <custom-attribute> in a zul.
<custom-attributes io.keikai.chart.emptyAsGaps="true"/>
Application Scope
zk.xml
<library-property>
<name>io.keikai.chart.emptyAsGaps</name>
<value>true</value>
</library-property>
Please read ZK Configuration Reference for details.
Limitation
- Currently, Spreadsheet cannot read the legend position from an XLS file.
Sparklines
Please see Features_and_Usages#sparklines
Rendering Customization
since 6.2.0
Keikai provides multiple powerful approaches to customize charts rendering, giving developers fine-grained control over chart rendering and styling.
Customization Scopes
Keikai supports 3 scopes of chart customization :
1. Application Scope
Configure a global chart customizer using a library property in zk.xml. That means keikai will apply this customizer to all charts in all spreadsheets.
<library-property>
<name>io.keikai.chart.customizer.class</name>
<value>io.keikai.devref.advanced.customization.chart.MyChartCustomizer</value>
</library-property>
2. Component Scope
Programmatically set a customizer for a specific spreadsheet:
// Apply a custom chart customizer to a spreadsheet
ChartsHelper.setCustomizer(spreadsheet, new MyChartCustomizer());
Then this customizer will be applied to all charts in this spreadsheet only.
3. Specific Chart Customization
Get a specific chart object(ZssCharts) and modify its options directly. You can get a chart:
- By its name:
ChartsHelper.getChartsByName(Spreadsheet spreadsheet, String name) - Iterate all charts:
ChartsHelper.getAllCharts(Spreadsheet spreadsheet)
ZssCharts is a subclass of ZK Charts and supports various chart options, see ZK Charts Essentials for details.
@Listen("onClick = #customize")
public void customizeChart() {
ZssCharts areaChart = ChartsHelper.getChartsByName(spreadsheet, "Chart 2");
if (areaChart != null) {
areaChart.setTitle("Programmatically Customized Chart");
}
}
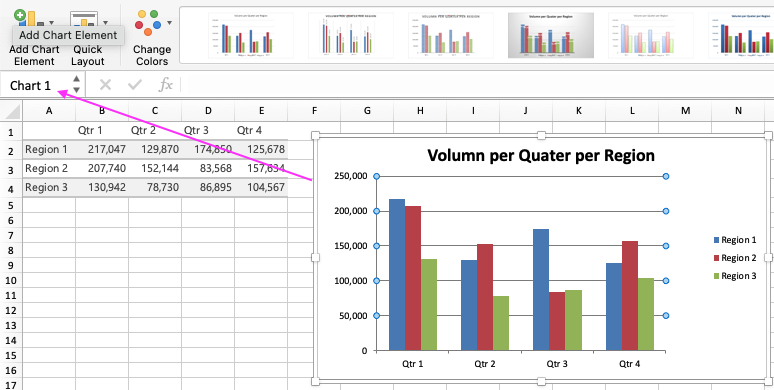
You can know a chart’s name in Excel by selecting the chart and looking at the Name Box in the top-left corner:
ChartsCustomizer Example
Here’s a complete example demonstrating chart customization:
public class MyChartCustomizer implements ChartsCustomizer {
@Override
public void customize(ZssCharts chart, SChart chartInfo) {
// Adjust plot options based on the chart type
if (chartInfo.getType()== SChart.ChartType.COLUMN) {
chart.setTitle("Customized Column Chart");
chart.getPlotOptions().getColumn().setStacking("normal");
// Customize series colors
chart.setColors(Arrays.asList(
new Color("#FFFF00"), // Yellow
new Color("#FFA500"), // Orange
new Color("#800080") // Purple
));
}
}
}
The customize() method provides access to two key objects:
ZssCharts: The chart component with rendering options that can be modifiedSChart: Read-only metadata about the chart’s configuration and data source
Best Practices
- Keep customization logic lightweight to avoid performance issues
- Use the
SChartparameter to make data-driven customization decisions
Limitations
- Notice that all customizations are applied on browser rendering only. It doesn’t affect the book model or XLSX exporting.
- The
SChartobject is read-only and cannot be modified - Customizations are applied before chart rendering in a browser
- Heavy-cost customizations may impact rendering performance